-
Presentation Middleware, Assignment 7.5
- The assignment:
-
-
- Establish an ODBC connection, which can be used for
requests between a client application and the DBMS used at our
institute.
Middleware, an overview
-
- As you must know by now, there are several types of
middleware:
-
- Remote Data Access (RDA), which implements a RDA
protocol for sending data manipulation language statements to an appropriate
database server for processing and transporting the result back to the
invoking process.
-
- Remote procedure calls (RPCs). RPC is used in most
network operating system services.
-
- Message-oriented middleware (MOM). MOM can be used as a
mechanism for storing and forwarding messages queuing.It can be used when
client and server processes communicate asynchronously.
-
- Object Request Brokers(ORBs). A standard implementation
of the ORB standard is CORBA. ORB makes it possible to invoke a remote
object by allowing a source object to send a message to that remote object.
-
- Distributed transaction processing (DTP). This type of
mechanism use execution semantics to interact between the client and the
server.
-
- Microsoft Open Database Connectivity (ODBC)
- ODBC is an open, vendor-neutral and powerful interface
that allows applications to seamlessly access over 50 different database
systems through a common set of functions. With this powerful technology,
developers don't need to learn multiple programming interfaces since they can use
the universal set of interfaces provided by ODBC.
- Microsoft's Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) interface
allows applications, through database drivers, access to data in a variety of
database management systems (DBMS). This allows users to evaluate their own
database environment and add ODBC database drivers without the need for
changes to the ODBC enabled application. MicroStation 95/MicroStation SE
provides a database server written with the ODBC interface. The MicroStation
server passes requests through an ODBC database driver to the underlying DBMS.
MicroStation does NOT deliver the ODBC database driver(s). The user is
responsible for purchasing ODBC database drivers for the DBMSs that need to be
accessed. There are several companies that provide ODBC drivers. These were
evaluated before development was started and the initial development and
testing has been done with Intersolv and Microsoft.
-
- Standards supported in Microsoft ODBC: ANSI SQL, ISO
9075, X/Open SQL CLI.
-
- ANSI SQL [ISO 9075-3]
ANSI SQL is a specification
for SQL from ANSI. American National Standards Institute (ANSI)
International Organization for Standardization (ISO)
- ISO 9075-3 [SQL/CLI]
ISO 9075-3 is a standard
from ISO based on the SQL Access Group (SAG) specification for Call Level
Interface (CLI).
-
In the picture below is showed how a connection is established using ODBC.
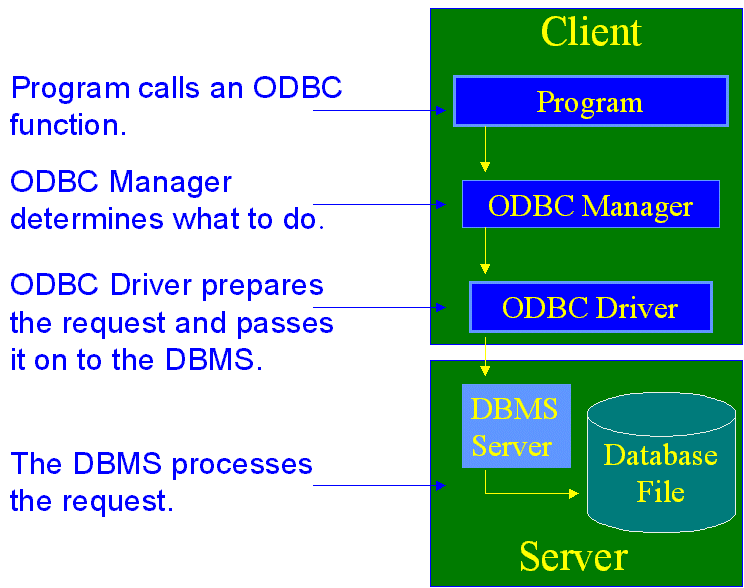
The Situation at School
- Here is a general description of the application, which is used
by the school's helpdesk. They have a database with entries based on the
users login names. In the database, problems with their history and solutions
are stored. The database also contains user-specific data. The database
is part of the school's Helpdesk application.
The helpdesk department has a Microsoft SQL Server running
on a Windows NT computer. The database is accessed by clients. The client
machines are using a program, which is running on Windows 95 machines. The
client makes a connection to the SQL server using ODBC. The used Client is
Support Magic by Magic Solutions.
Support Magic
- According to Magic Solutions, the vendor of Support Magic,
Support Magic is the industry's most popular user interface. It's a highly
integrated system with an open API. A robust, low-cost support solution that
can grow with a business. Whether the helpdesk supports 10 people or 1,000,
Network Associates delivers everything you need for success. With standard SQL
database support and a remarkably flexible interface, Magic Help Desk
SupportMagic Edition lets the administrator control everything without
programming. Designed for the small to mid-range internal helpdesk, Magic Help
Desk packs the power and versatility of an open, fully customizable database
into a low-maintenance, "out-of-the-box" support management
solution.
-
- It has the the following features:
- It provides comprehensive Help Desk
Functionality
- Powerful Web User Interface
- Advanced Knowledge Management can be done
- Customization
- Multiple Group Support
- User-friendly Database Administration
- End-user Self-service
Microsoft SQL Server
-
- With SQL Server for Windows NT, Microsoft created a database
engine that looked like SQL Server, walked like SQL Server and even quacked
like SQL Server, but which wasn't an ordinary SQL
server.
Microsoft rewrote SQL server to use native operating system services
for threads, memory management, disk I/O, symmetric multiprocessing support,
and even Windows NT's networking services. This was a complete break
with the past.
Microsoft SQL server uses threads. Instead of simulating threads
in the database kernel, as other servers did before, SQL Server used native
Win32 operating system threads - meaning that those threads ran in protected
memory spaces, preemptively scheduled by the Windows NT OS kernel. This
is called the Symmetric Server Architecture, which is shown here...
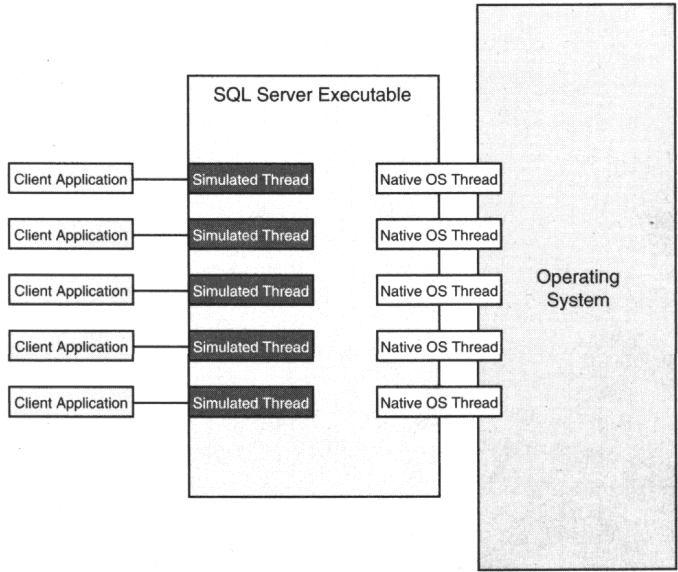
In Microsoft SQL Server a user connection is given a distinct thread
in the database kernel, but in Microsoft SQL Server on Windows NT, that
thread is a Win32 operating system thread. It's bound by the restrictions
of Windows NT's memory protection, thread scheduling, and
hardware-access rules, but it also has all the features of a Win32 thread . out
of the box support for multithreading, access to striped hardware devices, and
memory protection for individual threads. With this architecture, a single
corrupt thread no longer crashes the entire executable; instead, SQL Server can
trap the offending thread and continue execution.
Are there any special considerations for interfacing with
SQL Server?
- SQL Server does not recognize some ANSI SQL data types
such as number, numeric, decimal, integer, logical. The following data types
ARE recognized: money, smallmoney, int, smallint, tinyint, char(n),
varchar(n), text, datetime, smalldatetime, bit, timestamp, sysname, float,
real, binary(n), varbinary(n), image.
- SQL Server treats NULLs in a non ANSI manner. While ANSI
standards specify that a column by default can accept NULL values, in SQL
Server you must specify a column as NULL in order for it to accept NULL
values. The NOT NULL option on columns works as expected. This can lead to
problems with active entity creation. If a column in the active entity table
does not have a value, the active entity can not be inserted into a table
unless the create table statement defined the no value column with the NULL
option.
- The Intersolv ODBC SQL Server driver does not support SQL
statement over 2400 characters at this time.
- SQL Server 4.2 is supported on MicroStation 95. A new
ODBC server which provides SQL Server 6.5 support for MicroStation SE is
available. To use the new ODBC server, users are required to upgrade their
Microsoft ODBC drivers to version 3.51.
How is a connection established between the client and the
database on the SQL Server?
In the picture below can be seen what steps are taken to
make a connection:
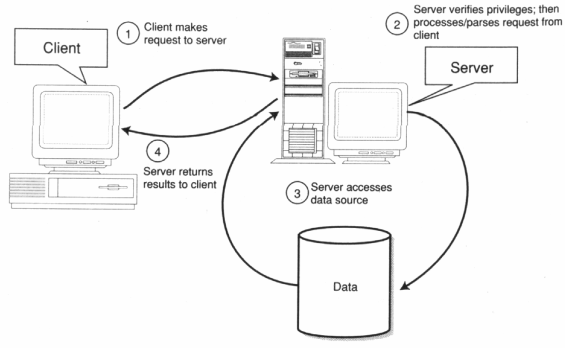
- A client makes a request to the server.
- The server verifies the client and processes and/or
parses the request.
- The server accesses the needed datasources.
- Finally, the server returns the results to the
client.
Conclusion
- Connection is made by using "Support Magic
Helpdesk" by Magic Solutions.
- The client establishes an ODBC connection.
- In principle it would be possible to use another
application, which also supports ODBC or even write your own client to access
the SQL server.
Questions
What kind of Middleware is ODBC?
What kind of Helpdesk application is used by the
school?
What happens if a thread gets corrupt?
Resources
Extra
This page: Copyright © 2000 Peter A. J. Troon.


